If your child is feeling overwhelmingly nervous or anxious about an upcoming trip to the dentist, you’ve likely started to explore your options when it comes to sedation dentistry. Here at Smile Cove Pediatric Dental, we offer three main types of sedation dentistry, and in this article, we’ll review what they are and when each type is recommended.
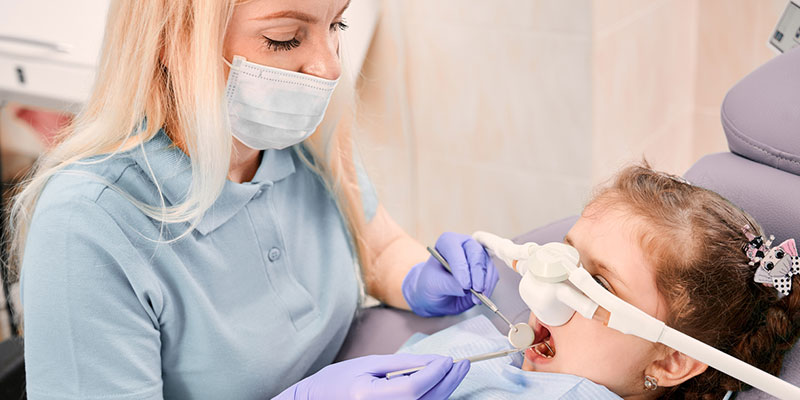
The mildest option of sedation dentistry we offer uses nitrous oxide, also known as “laughing gas”. This mild sedative is inhaled through a mask that is placed over the patient’s nose. Nitrous oxide does not cause a patient to lose consciousness completely but rather induces feelings of relaxation or euphoria that ease anxiety and allow for a non-traumatic dental procedure. Nitrous oxide is a great option for shorter procedures or for children whose anxiety or fear is mild, and the effects wear off much more quickly than other forms of sedation dentistry.
Next is oral sedation, which requires the patient to swallow a pill or drink a liquid sedative. The sedative must be taken prior to the appointment for the medication to take effect, and the effects may last for a few hours after the procedure is over. Because of this, it is extremely important for a responsible adult to accompany the child to their appointment and monitor them for several hours afterward. Oral sedation induces a deeper relaxation than nitrous oxide sedation and is good for easing moderate anxiety over a dental procedure.
Finally, IV sedation is used when a patient has severe anxiety over a dental procedure or when the procedure is expected to take a long time or is particularly complex. This method induces the deepest state of relaxation and allows the best control over the sedation level, thereby ensuring that the child is comfortable and unaware of the procedure being done. The IV sedative is administered by a trained dental anesthetist, who also closely monitors the child’s vital signs throughout the procedure. Patients may experience drowsiness for several hours after this type of sedation dentistry, so adult supervision and monitoring are required.
